CoffeeLoader is the latest malware loader observed in the wild, noted for its stealth and complexity. Emerging around September 2024, it delivers second-stage payloads while evading endpoint detection. Built for resilience, CoffeeLoader employs GPU-powered encryption, sleep obfuscation, and Windows fiber techniques to avoid forensic tools.
Related: Technical Analysis of Rhadamanthys Obfuscation Techniques
Key Takeaways
- CoffeeLoader delivers secondary payloads with precision.
- It evades EDR/AV using advanced techniques: spoofed call stacks, fiber-based execution, and encrypted memory.
- It utilizes a unique GPU-based packer, “Armoury,” inspired by ASUS software.
- A fallback domain generation algorithm (DGA) ensures persistent command-and-control.
- CoffeeLoader has been linked to SmokeLoader, and has deployed Rhadamanthys.
Technical Breakdown
The “Armoury” Malware Packer
This custom packer mimics ASUS’ Armoury Crate utilities. It hijacks DLL exports and executes shellcode that triggers GPU-based decryption using OpenCL:
__kernel void f(__global char* a,__global char* b,__global char* c,int d){
c[get_global_id(0)] = a[get_global_id(0)] ^ b[get_global_id(0) % d];
}
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Using hardcoded XOR strings and OpenCL, payloads remain hidden in memory until needed. This technique complicates static analysis and defeats basic virtualized environments.
Dropper Behavior
The dropper component can:
- Copy itself to
%PROGRAMDATA%or%LOCALAPPDATA% - Use
rundll32.exefor execution - Employ COM interface CMSTPLUA to bypass UAC
- Use Windows Task Scheduler (
schtasks.exe) or ITaskScheduler for persistence - Set file attributes (hidden, system, read-only)
- Lock access via
SetEntriesInAclW
Hash-based API resolution is used:
def hashval(val, initial_seed):
seed = initial_seed
for i in val.upper():
seed = (0xffffffff & (ord(i) + 33 * seed))
return seed
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)More on: How to manually remove malware
Stager Logic
The stager:
- Launches a suspended
dllhost.exe - Injects payload using
NtAllocateVirtualMemoryandNtWriteVirtualMemory - Alters thread context to trigger loader
Hashing continues here using a different seed (e.g., 0xF1).
CoffeeLoader Main Module Features
Call Stack Spoofing
The malware simulates legitimate call stacks using gadgets like jmp rbx, avoiding detection by tools that rely on stack tracing. It likely draws from BokuLoader.
Sleep Obfuscation
When idle, CoffeeLoader encrypts its memory with RC4:
- Heap + memory encrypted during sleep
- Memory restored before execution resumes
- Evasion of tools scanning memory during sleep cycles
It accounts for Control Flow Guard (CFG), dynamically allowing execution exceptions via NtSetInformationVirtualMemory.
Windows Fibers
Fibers offer manual multitasking in user mode. CoffeeLoader can shift between fibers, evading behavior-based detection tools.
C2 Communication
Over HTTPS, CoffeeLoader mimics iOS user agents. It uses:
- POST headers with encrypted RC4 binary blobs
- Certificate pinning to block TLS inspection
- Custom message types (0x69 = registration, 0x42 = tasking)
typedef struct coffee_header {
DWORD msg_size;
DWORD magic_bytes; // 0xc0ffee42
DWORD bot_id;
DWORD msg_type;
} coffee_header;
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Command IDs:
| ID | Description |
|---|---|
| 0x58 | Sleep |
| 0x87 | Inject shellcode |
| 0x89 | Update sleep technique |
| 0x91 | Run EXE payload from temp |
| 0x93 | Run DLL payload using rundll32.exe |
DGA (Domain Generation Algorithm)
Fallback domains are generated daily. Sample code:
def rand(seed):
return (0x41C64E6D * seed + 0x3039) & 0x7FFFFFFF
def generate(year, month, day):
return str(rand(33 * (33 * year + month) + day)) + ".com"
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)SmokeLoader Parallels
CoffeeLoader overlaps heavily with SmokeLoader:
- Identical persistence strategy
- Hash-based API resolution
- RC4-encrypted network traffic
- Use of low-level
NtandZwfunctions - Scheduled task executes every 10 minutes
Still, no confirmed link has been established beyond behavioral resemblance.
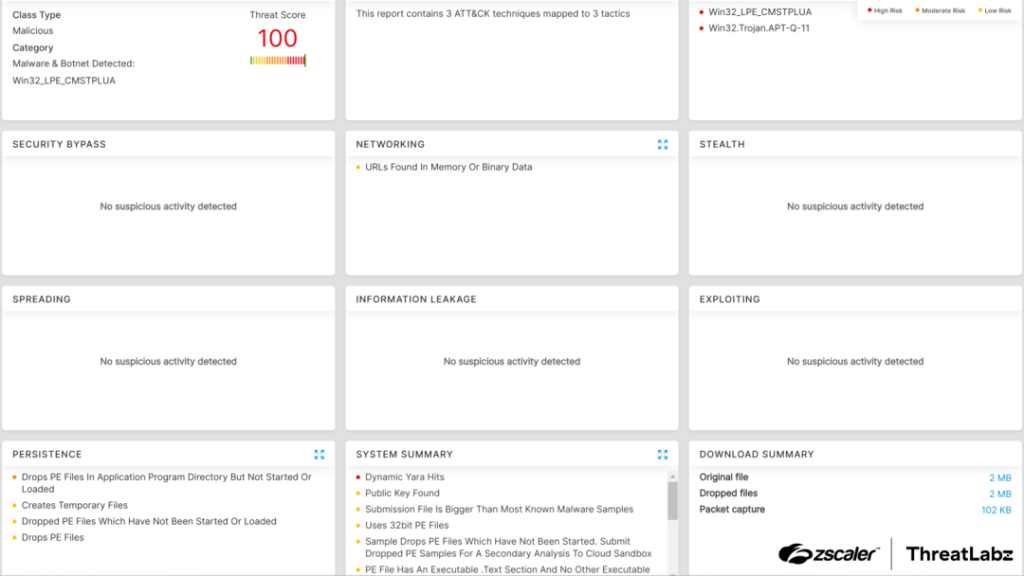
Zscaler Detection
Zscaler detects CoffeeLoader via sandbox and real-time scanning. Threat names include:
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
| Indicator | Description |
|---|---|
https://freeimagecdn[.]com/ | C2 server |
https://mvnrepo[.]net/ | C2 server |
| SHA256 hashes: | Various CoffeeLoader binaries |
c930eca887fdf45aef9553c258a403374c51b9c92c481c452ecf1a4e586d79d9 | Loader payload (SHA256) |
8941b1f6d8b6ed0dbc5e61421abad3f1634d01db72df4b38393877bd111f3552 | Loader payload (SHA256) |
5538b88eb2effa211a9c324b001e02802b7ccd0008b3af9284e32ab105dc9e6f | Loader payload (SHA256) |
70fafd3fefca2fd4a061d34e781136f93a47d856987832041d3c703658d60fc1 | Loader payload (SHA256) |
| bc1b750338bc3013517e5792da59fba0d9aa3965a9f65c2be7a584e9a70c5d91 | Loader payload (SHA256) |
| 5fcd2e12723081f512fa438301690fb310610f4de3c191c7c732d56ece7f0499 | Loader payload (SHA256) |
Final Thoughts
CoffeeLoader is more than just a typical loader. Its stealth toolkit, layered execution model, and ties to mature malware families position it as a top-tier threat. Its development hints at red team expertise, drawing heavily from public research.
Security teams must remain proactive. Threats like CoffeeLoader require layered defenses, behavior analytics, and constant vigilance.

